Gonorrhea or chlamydia as it is also known, is a disease that is transmitted through sexual contact.
According to statistics, the incidence of gonorrhea has doubled in the last decade.
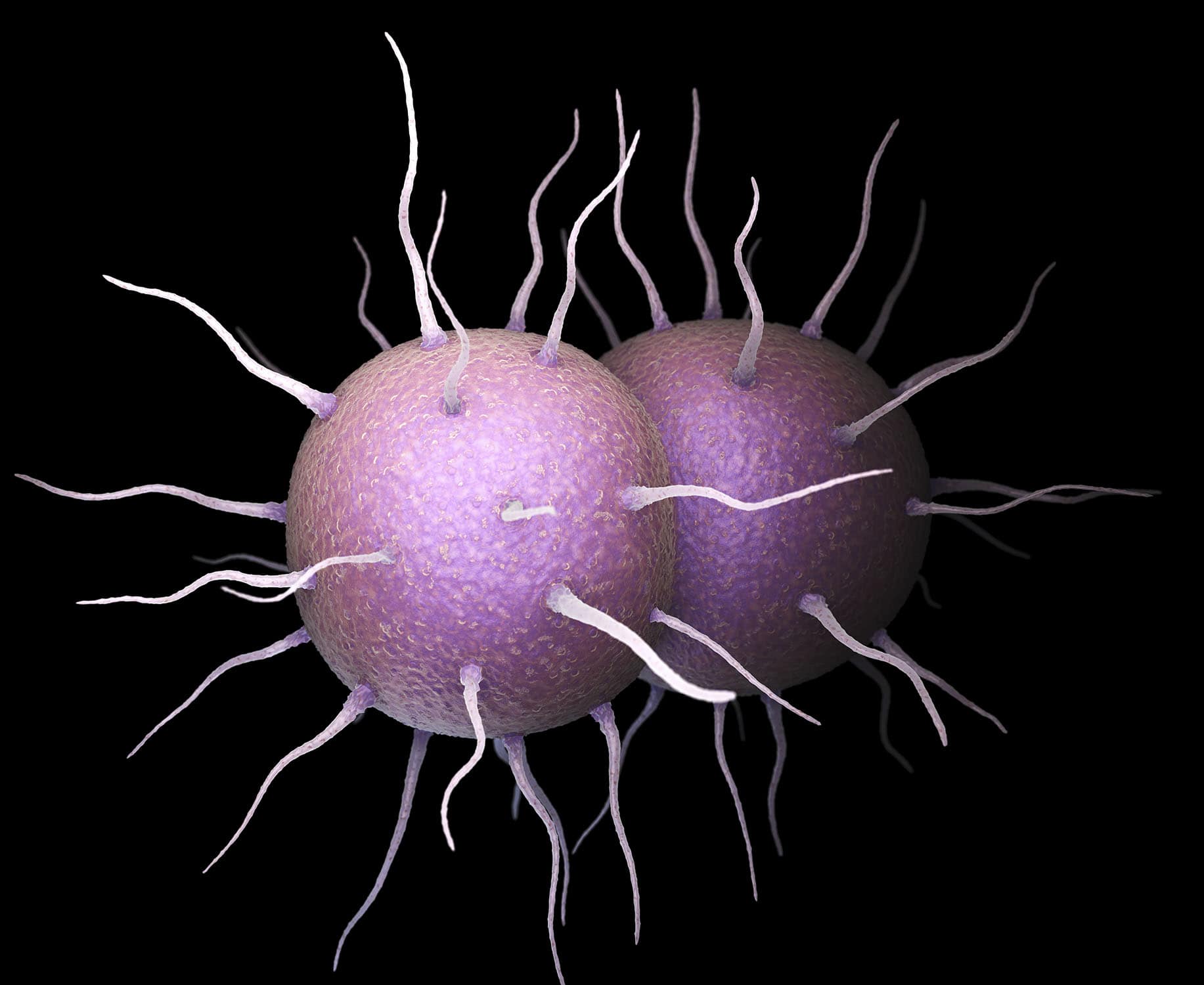
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Is transmitted from person to person during sexual activity of any kind.
A lot of people who contract gonorrhea may not have symptoms. This situation, there is a more frequently in women than in men.
When there are symptoms that occur about 10 days after the transmission of and infection by the bacterium.
Men may appear purulent secretions coming out of the urethra. While it may appear redness at the opening of the urethra, itching, frequent urination, pain and καυσος during urination.
In women can manifest pain or κάυσος during urination, frequent urination, vaginal discharge that is purulent with bad smell and discomfort in the perianal area.In 15% of women, the bacteria will spread to the uterus and the fallopian tubes. The attack of the fallopian tubes may be the cause of sterilization in female. During copulation, the woman may have pain. It is also possible to have a loss of blood during her period, fever, and abdominal pain.
If gonorrhea is left without proper treatment it is possible to cause in men prostatitis is an inflammation and infection of the prostate. Also it is possible to cause epididymitis and orchitis. In women if left without treatment, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease with vaginosis and risk of sterilization.
The arthritis observed in gonorrhoea, can affect one or more joints. May be affected large joints such as the knees and hip joints. There is pain and a reduction in the functionality of the joint.
Pregnant women who contract gonorrhea if remain without treatment, it is possible to transmit the bacteria to their child. In the newborn the gonococcus is causing the gonococcal οφθαλμίτιδα. This is a very serious infection of the eyes of the child. The disease occurs in 1 to 4 days after birth and can affect one or both eyes. The newborn presents in these cases, bloodshot eyes, swelling of the eyelashes and secretions from the eyes that is purulent.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on history, clinical picture, which includes the signs and symptoms of the patient,the microbiological examination and the cultures of pathological secretions, which can indicate whether or not the gonococcus.
Treatment
Antibiotics of the family of cephalosporins (cefixime, ceftriaxone), or other antibiotics such as amoxycillin-clavulanic acid, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and azithromycin is effective against γονοκόκκου. After the initial administration of antibiotics should be re-checked because there is the possibility that the gonococcus has resistance to some antibiotics and thus a need for an adjustment of therapy.
The cases of patients infected by more than one sexually transmitted disease is not rare. For this reason, if you become a diagnosis of someone suffering from such a disease, you need to check whether it has been infected by other .
Pregnant women should be tested for gonorrhea with the purpose of prevention of γονοκοκκικής οφθαλμίτιδας.
The prevention is based on the use of a condom. The sexual relations with only one sexual partner who is not infected by the gonococcus, are also an effective prevention.